HSE Scientist Optimises Solution of Hydrodynamics Problems

Supercomputers are no longer required to calculate fluid flows in multiscale problems.
Roman Gaydukov, Associate Professor at the MIEM HSE School of Applied Mathematics, has modelled the fluid flow around a rotating disk with small surface irregularities. His solution allows for predicting fluid flow behaviour without the need for powerful supercomputers. The results have been published in Russian Journal of Mathematical Physics.
Hydrodynamics studies the motion of fluids and their interaction with solid surfaces. This branch of physics makes it possible to understand and predict the behaviour of fluids and gases under various conditions. In particular, the principles of hydrodynamics are used in electrochemistry for calculating the reactions of galvanisation, such as silver molecules adhering to a metal surface, and oxidation, such as patina formation on copper.
These processes use a disk electrode, which is a flat metal plate that rotates in a fluid. To accurately calculate electrochemical reactions, it is essential to understand how the fluid moves around the electrode and what conditions that need to be maintained. To achieve this, scientists must account for numerous variables, while even minor irregularities on the disk surface can greatly influence fluid flow, leading to complex and unexpected effects.
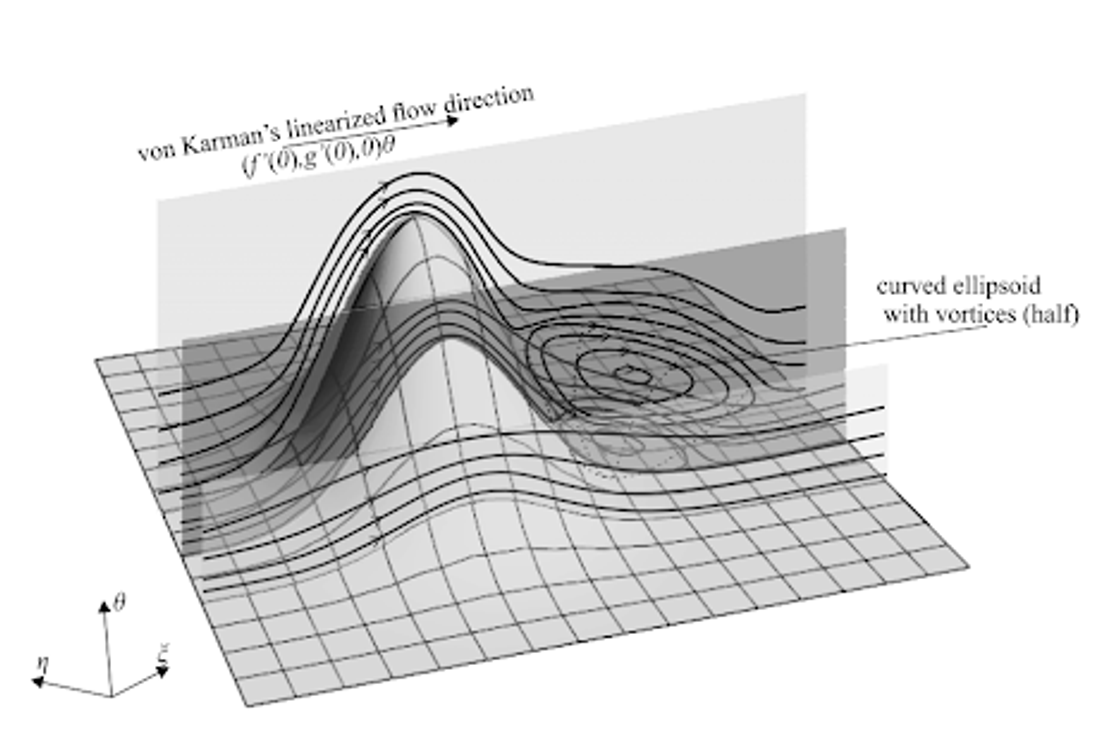
Earlier studies focused solely on symmetrical irregularities, but a scientist at HSE University examined a more complex case. Roman Gaydukov calculated how fluid flow would change with the presence of asymmetrical irregularities on the rotating disk surface.
To do this, he used the method of multideck structures of boundary layers, making it possible to decompose the three-dimensional problem into a series of two-dimensional ones. This method helps solve complex hydrodynamic problems at high Reynolds numbers, where direct modelling is impossible. Although this method has been known since the late 1960s, a rigorous mathematical formulation was only recently developed by the author of the paper together with Professor Vladimir Danilov. The mathematical algorithm of the method can be integrated into any symbolic computation software.

Roman Gaydukov
'Under real conditions, perfectly smooth surfaces do not exist. We have demonstrated how small irregularities on the disk surface affect fluid flow by creating vortex zones and altering the structure of the boundary layer,' explains Roman Gaydukov. 'Our method allows modelling a problem within a few hours, whereas it could take days or even weeks on a supercomputer. This not only saves time but also reduces the cost of computational resources. The method works effectively for large but finite Reynolds numbers.'
The Reynolds number is a dimensionless quantity that describes the relationship between inertial and viscous forces in fluid flow. A large Reynolds number signifies the dominance of inertial forces, which often results in turbulent (chaotic) flows, while a small Reynolds number indicates the dominance of viscous forces, leading to laminar (ordered) flows.
The developed approach can be used to accurately model fluid motion during chemical reactions, with potentially wide applications in industry.
In the future, the scientist plans to extend his research to more complex systems involving interactions between different phases, such as liquid droplets in an air stream or aerosols. This will enable a deeper understanding of the processes in multicomponent and multiphase systems and help improve existing models.
According to Gaydukov, 'Together with my graduate student Nikita Burov, we plan to investigate how the shape of fluid droplets changes as they move through an air flow and how the droplets, as irregularities—including their potential freezing—affect the flow.'
See also:
Script Differences Hinder Language Switching in Bilinguals
Researchers at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain used eye-tracking to examine how bilinguals switch between languages in response to context shifts. Script differences were found to slow down this process. When letters appear unfamiliar—such as the Latin alphabet in a Russian-language text—the brain does not immediately switch to the other language, even when the person is aware they are in a bilingual setting. The article has been published in Bilingualism: Language and Cognition.
HSE Experts Highlight Factors Influencing EV Market Growth
According to estimates from HSE University, Moscow leads in the number of charging stations for electric vehicles in Russia, while Nizhny Novgorod ranks first in terms of charging station coverage, with 11.23 electric vehicles per charging station, compared to 14.41 in Moscow. The lack of charging infrastructure is one of the key factors limiting the growth of the electric vehicle market. This is stated in the study titled ‘Socio-Economic Aspects of Introducing Electric Vehicles in Commercial Transportation’ conducted by experts from the Institute of Transport Economics and Transport Policy Studies at HSE University.
Machine Learning Links Two New Genes to Ischemic Stroke
A team of scientists from HSE University and the Kurchatov Institute used machine learning methods to investigate genetic predisposition to stroke. Their analysis of the genomes of over 5,000 people identified 131 genes linked to the risk of ischemic stroke. For two of these genes, the association was found for the first time. The paper has been published in PeerJ Computer Science.
First Digital Adult Reading Test Available on RuStore
HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain has developed the first standardised tool for assessing Russian reading skills in adults—the LexiMetr-A test. The test is now available digitally on the RuStore platform. This application allows for a quick and effective diagnosis of reading disorders, including dyslexia, in people aged 18 and older.
Low-Carbon Exports Reduce CO2 Emissions
Researchers at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences and the Federal Research Centre of Coal and Coal Chemistry have found that exporting low-carbon goods contributes to a better environment in Russian regions and helps them reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The study results have been published in R-Economy.
Russian Scientists Assess Dangers of Internal Waves During Underwater Volcanic Eruptions
Mathematicians at HSE University in Nizhny Novgorod and the A.V. Gaponov-Grekhov Institute of Applied Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences studied internal waves generated in the ocean after the explosive eruption of an underwater volcano. The researchers calculated how the waves vary depending on ocean depth and the radius of the explosion source. It turns out that the strongest wave in the first group does not arrive immediately, but after a significant delay. This data can help predict the consequences of eruptions and enable advance preparation for potential threats. The article has been published in Natural Hazards. The research was carried out with support from the Russian Science Foundation (link in Russian).
Centre for Language and Brain Begins Cooperation with Academy of Sciences of Sakha Republic
HSE University's Centre for Language and Brain and the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) have signed a partnership agreement, opening up new opportunities for research on the region's understudied languages and bilingualism. Thanks to modern methods, such as eye tracking and neuroimaging, scientists will be able to answer questions about how bilingualism works at the brain level.
How the Brain Responds to Prices: Scientists Discover Neural Marker for Price Perception
Russian scientists have discovered how the brain makes purchasing decisions. Using electroencephalography (EEG) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), researchers found that the brain responds almost instantly when a product's price deviates from expectations. This response engages brain regions involved in evaluating rewards and learning from past decisions. Thus, perceiving a product's value is not merely a conscious choice but also a function of automatic cognitive mechanisms. The results have been published in Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
AI Predicts Behaviour of Quantum Systems
Scientists from HSE University, in collaboration with researchers from the University of Southern California, have developed an algorithm that rapidly and accurately predicts the behaviour of quantum systems, from quantum computers to solar panels. This methodology enabled the simulation of processes in the MoS₂ semiconductor and revealed that the movement of charged particles is influenced not only by the number of defects but also by their location. These defects can either slow down or accelerate charge transport, leading to effects that were previously difficult to account for with standard methods. The study has been published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
Electrical Brain Stimulation Helps Memorise New Words
A team of researchers at HSE University, in collaboration with scientists from Russian and foreign universities, has investigated the impact of electrical brain stimulation on learning new words. The experiment shows that direct current stimulation of language centres—Broca's and Wernicke's areas—can improve and speed up the memorisation of new words. The findings have been published in Neurobiology of Learning and Memory.