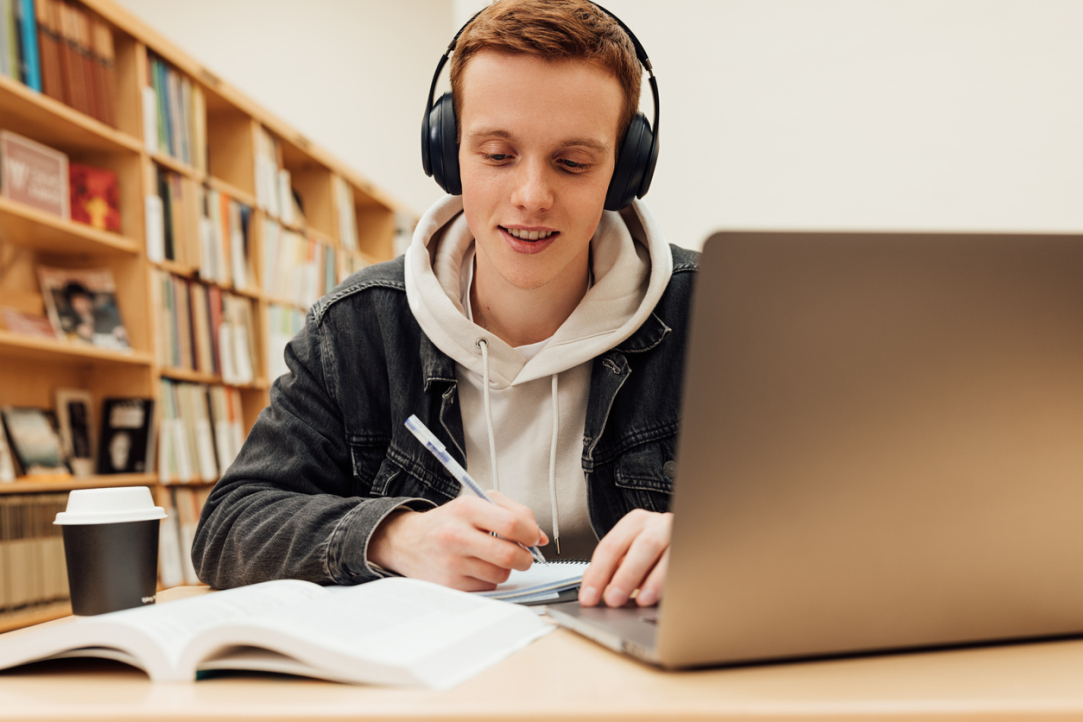
HSE Researchers Offer Guidance to Prevent Undergraduate Burnout
Researchers at the HSE Institute of Education have identified how much time students should ideally devote to their studies, extracurricular activities, and personal life to maintain strong academic performance without compromising their mental health. An analysis of responses from 2,753 students, combined with their actual academic results, revealed several risk factors—such as excessive homework—as well as positive factors, including sufficient sleep, regular exercise, and moderate participation in projects. Based on these findings, the researchers developed practical recommendations for both students and universities. The paper has been published in the European Journal of Education.

HSE University–St Petersburg Holds First International School for Early-Career Researchers in Arab Studies
HSE University–St Petersburg has held the first 'Contemporary Studies of the Sultanate of Oman: Methods, Concepts, Texts' international school for early-career researchers. The programme gathered more than 30 students and experts from Russia, Oman, Italy, and France.

Scientists Discover Why Parents May Favour One Child Over Another
An international team that included Prof. Marina Butovskaya from HSE University studied how willing parents are to care for a child depending on the child’s resemblance to them. The researchers found that similarity to the mother or father affects the level of care provided by parents and grandparents differently. Moreover, this relationship varies across Russia, Brazil, and the United States, reflecting deep cultural differences in family structures in these countries. The study's findings have been published in Social Evolution & History.

When a Virus Steps on a Mine: Ancient Mechanism of Infected Cell Self-Destruction Discovered
When a virus enters a cell, it disrupts the cell’s normal functions. It was previously believed that the cell's protective response to the virus triggered cellular self-destruction. However, a study involving bioinformatics researchers at HSE University has revealed a different mechanism: the cell does not react to the virus itself but to its own transcripts, which become abnormally long. The study has been published in Nature.

Artificial Intelligence Transforms Employment in Russian Companies
Russian enterprises rank among the world’s top ten leaders in AI adoption. In 2023, nearly one-third of domestic companies reported using artificial intelligence. According to a new study by Larisa Smirnykh, Professor at the HSE Faculty of Economic Sciences, the impact of digitalisation on employment is uneven: while the introduction of AI in small and large enterprises led to a reduction in the number of employees, in medium-sized companies, on the contrary, it contributed to job growth. The article has been published in Voprosy Ekonomiki.

Lost Signal: How Solar Activity Silenced Earth's Radiation
Researchers from HSE University and the Space Research Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences analysed seven years of data from the ERG (Arase) satellite and, for the first time, provided a detailed description of a new type of radio emission from near-Earth space—the hectometric continuum, first discovered in 2017. The researchers found that this radiation appears a few hours after sunset and disappears one to three hours after sunrise. It was most frequently observed during the summer months and less often in spring and autumn. However, by mid-2022, when the Sun entered a phase of increased activity, the radiation had completely vanished—though the scientists believe the signal may reappear in the future. The study has been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics.

Banking Crises Drive Biodiversity Loss
Economists from HSE University, MGIMO University, and Bocconi University have found that financial crises have a significant negative impact on biodiversity and the environment. This relationship appears to be bi-directional: as global biodiversity declines, the likelihood of new crises increases. The study examines the status of populations encompassing thousands of species worldwide over the past 50 years. The article has been published in Economics Letters, an international journal.
.jpg)
Scientists Discover That the Brain Responds to Others’ Actions as if They Were Its Own
When we watch someone move their finger, our brain doesn’t remain passive. Research conducted by scientists from HSE University and Lausanne University Hospital shows that observing movement activates the motor cortex as if we were performing the action ourselves—while simultaneously ‘silencing’ unnecessary muscles. The findings were published in Scientific Reports.

Russian Scientists Investigate Age-Related Differences in Brain Damage Volume Following Childhood Stroke
A team of Russian scientists and clinicians, including Sofya Kulikova from HSE University in Perm, compared the extent and characteristics of brain damage in children who experienced a stroke either within the first four weeks of life or before the age of two. The researchers found that the younger the child, the more extensive the brain damage—particularly in the frontal and parietal lobes, which are responsible for movement, language, and thinking. The study, published in Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology, provides insights into how age can influence the nature and extent of brain lesions and lays the groundwork for developing personalised rehabilitation programmes for children who experience a stroke early in life.

Scientists Test Asymmetry Between Matter and Antimatter
An international team, including scientists from HSE University, has collected and analysed data from dozens of experiments on charm mixing—the process in which an unstable charm meson oscillates between its particle and antiparticle states. These oscillations were observed only four times per thousand decays, fully consistent with the predictions of the Standard Model. This indicates that no signs of new physics have yet been detected in these processes, and if unknown particles do exist, they are likely too heavy to be observed with current equipment. The paper has been published in Physical Review D.